THE LIOEXTRACTION PROCESS
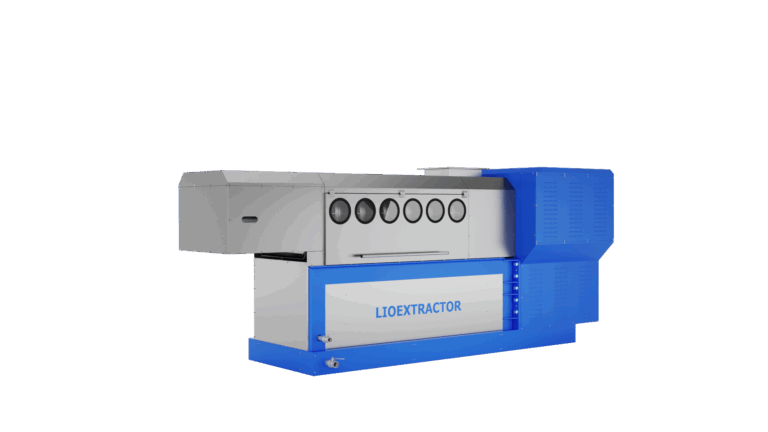
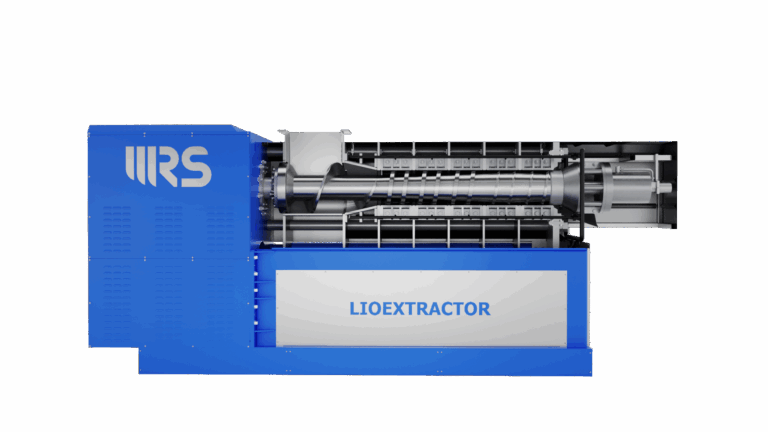
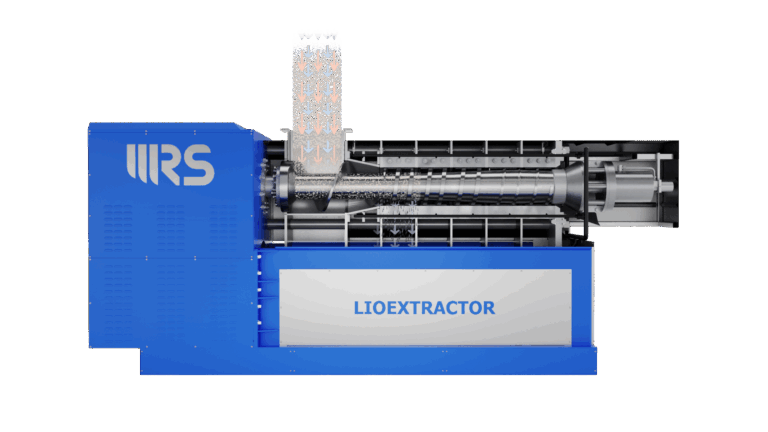
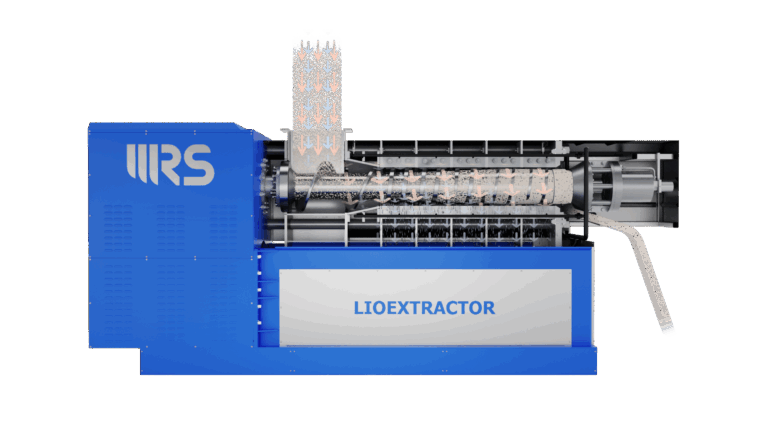
The WRS Lioextractor mechanically presses and dehydrates all types of compressible materials — including woody biomass, pulper waste, biogas digestate, compost, treatment residues, agricultural waste, and FORSU.
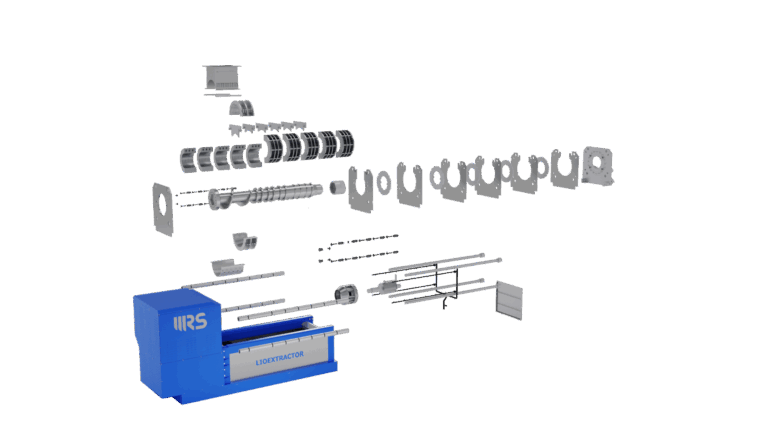
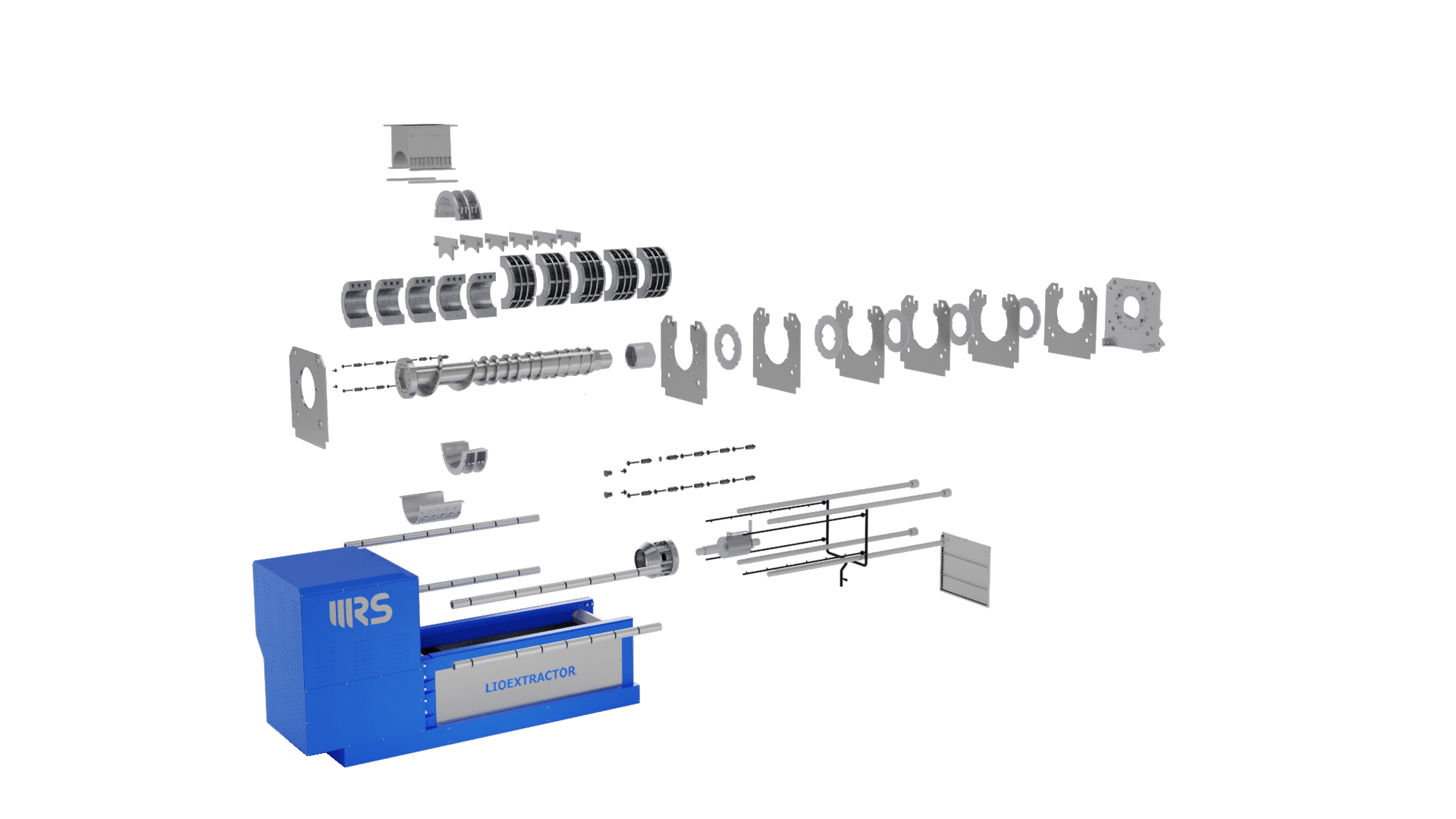
Main Components
- Pressing system with a discontinuous-pitch compression screw and two half-shell filter modules for quick and easy replacement;
- Control unit with an electric motor and a transmission system comprising a gearbox and V-belts;
- Hydraulic system with a power unit for counter-thrust regulation;
- Electrical system with PLC-based control panel, protections, and safety devices compliant with current regulations;
- Automatic washing system to keep all filtering surfaces clean;
- Liquid collection tank for process management.

FIELDS OF APPLICATION
The WRS Lioextractor can be effectively used in:
- Paper mill pulper waste
- Biogas digestate
- Waste treatment residue
- Woody biomass
- Agricultural by-products
- Compost
- FORSU
MAIN ADVANTAGES
By choosing the WRS SW500/6 Lioextractor, you can benefit from:
LOWER OPERATING COSTS,
thanks to reduced material weight, volume, and transport needs
HOMOGENEOUS, OPTIMIZED OUTPUT,
producing a liquid fraction and a highly dehydrated, shredded solid fraction — ideal for transport, reuse, and energy recovery;
INTEGRATED AUTOMATION,
with intelligent control systems adapting to input material characteristics;
INNOVATIVE COMBINED DEHYDRATION AND CRUSHING SYSTEM
achieving minimal residual moisture and maximum volume reduction;
ADVANCED MONITORING SOFTWARE,
managing outlet moisture and coordinating motor load with hydraulic counter-pressure;
AUTOMATIC FILTER WASHING SYSTEM,
maintaining high discharge efficiency over time;
QUICK AND EASY MAINTENANCE,
with simplified disassembly of filters and compression screws, minimizing downtime.
FOCUS: BENEFITS FOR AGRICULTURE AND BIOGAS
The Lioextractor is particularly effective in the agricultural and biogas sectors, thanks to its high-efficiency solid-liquid separation of digestate, which optimizes nutrient recovery and reduces operating costs.
Key benefits include:
- Improved storage management;
- Enhanced transport efficiency due to reduced volume and weight;
- Lower soil compaction during field application;
- Optimized agronomic use, allowing for more precise and sustainable nutrient distribution;
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions during storage and spreading;
- Promotion of circular economy practices, enabling nutrient recycling within agricultural cycles;
- Improved soil quality, enhancing structure, fertility, and water retention;
- Better animal welfare, as the solid fraction (with ~45% residual moisture) provides dry, comfortable bedding that reduces infection risk;
- Odor reduction, improving environmental quality and facilitating use even near urban areas.